BIO- UND HYBRIDPOLYMERE
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-001 | 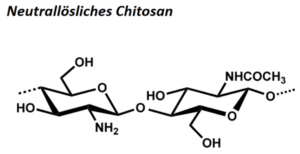 |
neutrallösliches Chitosan | verschiedene hoch- und niedrigviskose Chitosane (Edukt) | DD im Bereich 40 – 60 % | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-002 | 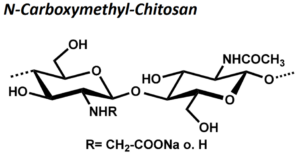 |
N-Carboxymethyl-Chitosan | verschiedene hoch- und niedrigviskose Chitosane (Edukt) | ca. 90 % der freien NH2-Gruppen carboxymethyliert | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-003 | 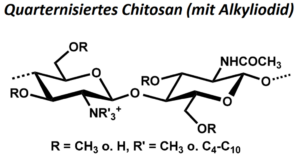 |
Chitosan, quarternisiert (mit Alkyliodid) | verschiedene hoch- und niedrigviskose Chitosane (Edukt) | variabel | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-004 | 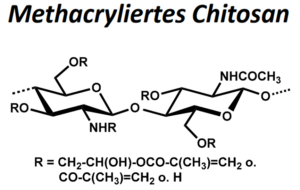 |
methacrylierte Chitosanderivate | verschiedene hoch- und niedrigviskose Chitosane (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad DD = Deacetylierungsgrad
Weitere Informationen zu funktionalisierten Chitosanen und Polysaccharidderivaten finden Sie hier.
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-005 | 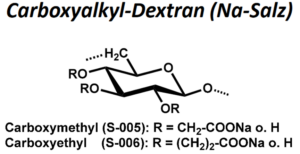 |
Carboxymethyl-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) |
einfache CM: DS ca. 0,6 – 0,8 zweifache CM: DS ca. 0,9 – 1,1 dreifache CM: DS ca. 1,2 – 1,4 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-006 | 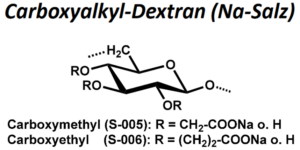 |
Carboxyethyl-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) | DS ≤ 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-007 | 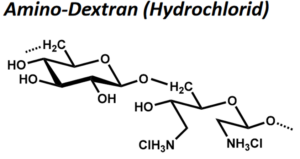 |
Amino-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) | NH2-Gehalt: variabel, 80 – 350 µmol/g | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-008 | 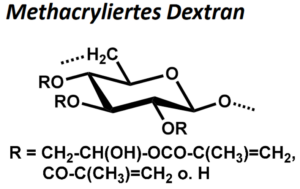 |
Methacryliertes Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-009 | 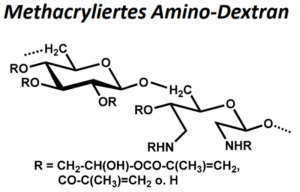 |
Methacryliertes Amino-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) |
DS (M) < 1 NH2-Gehalt: 10 – 50 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-010 | 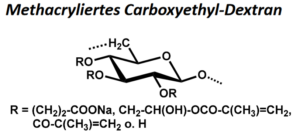 |
Methacryliertes Carboxyethyl-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) |
DS (CE) ≤ 1 DS (M) < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-011 | 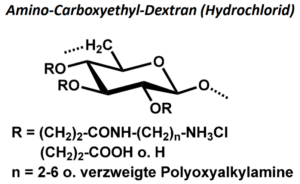 |
Amino-Carboxyethyl-Dextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) |
DS (CE) ≤ 1 NH2-Gehalt: variabel, 100 – 1200 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-012 | 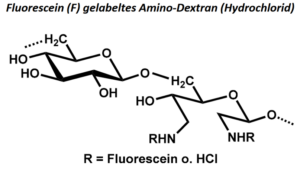 |
Fluorescein gelabeltes Aminodextran | 20, 100 bzw. 500 (Edukt) |
DS (F) < 1 NH2-Gehalt: variabel, 20 – 250 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad
Weitere Informationen zu funktionalisierten Dextranen und Polysaccharidderivaten finden Sie hier
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-013 | 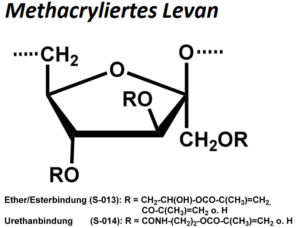 |
Methacryliertes Levan (Ether/Ester) | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-014 |  |
Methacryliertes Levan (Urethan) | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-015 | 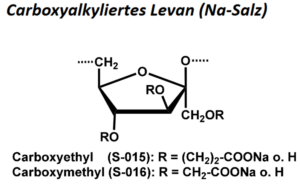 |
Carboxyethyl-Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS ≤ 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-016 |  |
Carboxymethyl-Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS < 1,2 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-017 | 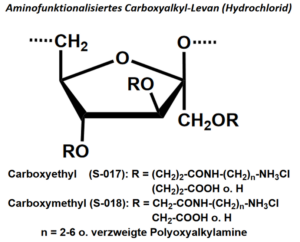 |
Aminofunktionalisiertes Carboxyethyl-Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) |
DS (CE) ≤ 1 NH2-Gehalt: variabel, 40 – 600 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-018 |  |
Aminofunktionalisiertes Carboxymethyl-Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) |
DS (CE) < 1,2 NH2-Gehalt: variabel, 90 – 380 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-019 | 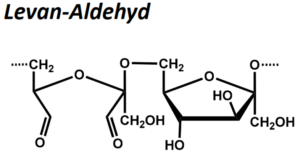 |
Levan-Aldehyd | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) |
Oxidation variabel |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-020 | 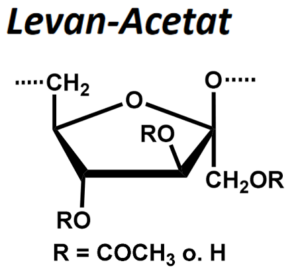 |
Levanacetat | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) |
DS ≤ 3 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-021 | 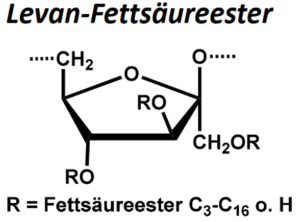 |
Levan-Fettsäureester | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-022 | 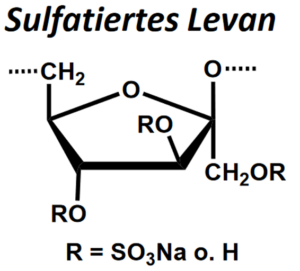 |
Sulfatiertes Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS ≤ 2 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-023 | 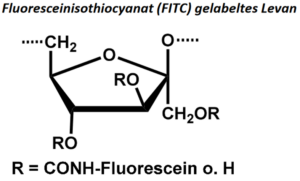 |
FITC gelabeltes Levan | 600 – 1000 (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad
Weitere Informationen zu funktionalisierten Levanen und Polysaccharidderivaten finden Sie hier
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-024 | 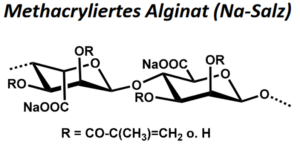 |
Methacryliertes Natrium-Alginat | 100 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad
Weitere Informationen zu funktionalisierten Natrium-Alginaten und Polysaccharidderivaten finden Sie hier.
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-027 (a-c) | 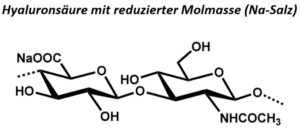 |
Hyaluronsäure mit reduzierter Molmasse |
300 – 700 80 – 150 20 – 50 |
entfällt |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-028 (a, b) | 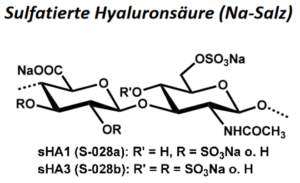 |
Sulfatierte Hyaluronsäure |
20 – 50 50 – 2000 |
sHA1: DS ca. 1 – 1,4 sHA3: DS > 3 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-029 | 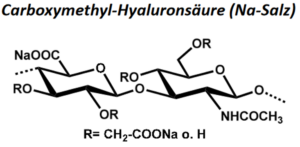 |
Carboxymethyl-Hyaluronsäure | 12 – 20 | DS ca. 0,5 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-030 | 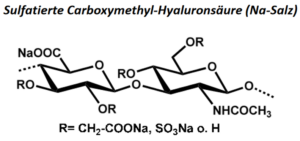 |
Sulfatierte Carboxymethyl-Hyaluronsäure | 10 – 20 |
DS (CM) ca. 0,5 DS (S) ca. 3 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-031 | 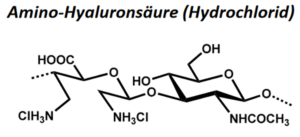 |
Amino-Hyaluronsäure | 13 – 20 |
NH2-Gehalt: variabel, ca. 200 – 400 µmol/g |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-032 | 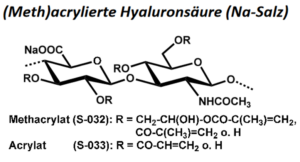 |
Methacrylierte Hyaluronsäure | 30 – 1000 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-033 |  |
Acrylierte Hyaluronsäure | 20 – 100 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-034 | 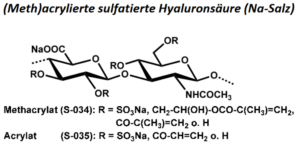 |
Methacrylierte sulfatierte Hyaluronsäure | 20 – 50 (Edukt) |
DS (S) ca. 1 – 1,4 DS (M) < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-035 |  |
Acrylierte sulfatierte Hyaluronsäure | 20 – 50 (Edukt) |
DS (S) ca. 1 – 1,4 DS (A) < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-036 | 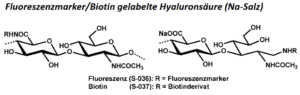 |
Fluoreszenz gelabelte Hyaluronsäure | variabel | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-037 |  |
Biotin gelabelte Hyaluronsäure | variabel | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad
Weitere Informationen zu funktionalisierten Hyaluronsäuren und Glycoyaminoglycanen finden Sie hier
| Referenz-Nummer | Formel | Substanz | Molmasse | Funktionalisierungsgrad | Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-038 |  |
Methacryliertes Polyglycerin (Ether/Ester) |
1 – 20 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-039 |  |
Methacryliertes Polyglycerin (Urethan) |
1 – 20 (Edukt) |
DS < 1 |
Datenblatt |
| BMA-S-040 |  |
Polyglycerin-Fettsäureester | 1 – 20 (Edukt) | DS < 1 | Datenblatt |
DS = durchschnittlicher Substitutionsgrad
Gern übernehmen wir Ihre Auftragssynthesen!
Unser erfahrenes und chemisch-technisch versiertes Team begleitet komplexe Projekte auf dem Gebiet der Auftragssynthese / Auftragsforschung von der ersten Planung bis zur optimalen Lösung. Sowohl kundenspezifische Syntheseanfragen als anspruchsvolle chemische Trennprobleme sind bei SYNPROLAB in zuverlässigen und kompetenten Händen. Wir freuen uns auf Ihre Anfrage!
